Как установить sqlite linux
Как установить SQLite и браузер SQLite в Ubuntu
SQLite — это легкая, небольшая и автономная СУБД. Популярные базы данных, такие как MySql, PostgreSQL и т. д. работают как клиент — сервер, и у них есть специальный процесс, выполняющий и контролирующий все аспекты работы базы данных.
SQLite используется в таких программах как:
Областей где используется SQLite очень много. Например каждый смартфон в мире имеет сотни файлов базы данных SQLite. На наш взгляд это довольно большое количество. Пока приступить к установке db.
Установка SQLite в Ubuntu
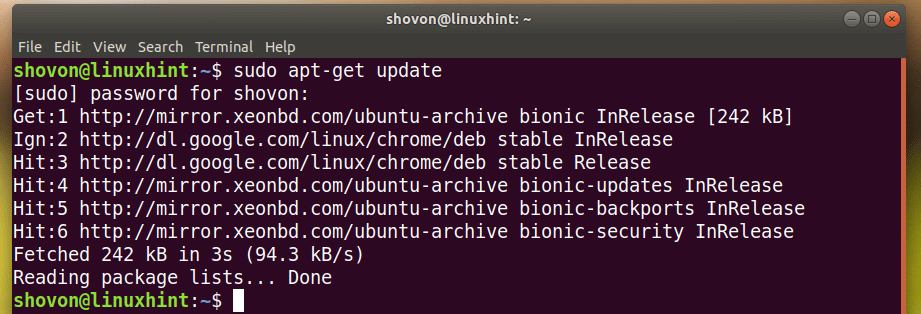
Настройка и установка SQLite очень проста, по сравнению с другими популярными базами данных, такими как MySql, Postgresql и т. д. Во-первых, обновите apt-cache, выполнив следующую команду.
Теперь проверьте, есть ли какие нибудь пакеты SQLite, которые доступны в репозитории apt. Для этого выполнив следующую команду.
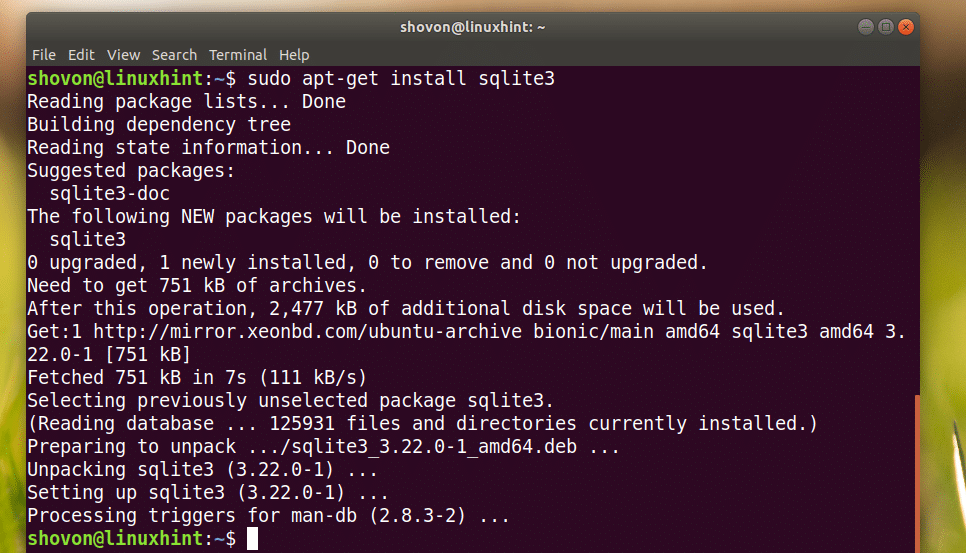
Чтобы установить SQLite, выполните следующую команду.
Вы можете проверить установку, для этого запустите сеанс sqlite. Это можно сделать выполнив следующую команду.
Как видно из приведенного выше изображения, SQLite3 успешно установлен и работает с версией 3.33.0..
Создание базы данных и таблицы SQLite
База данных хранится в виде файла в вашей файловой системе. Вы можете создать базу данных при запуске сеанса sqlite, указав имя базы данных в качестве аргумента. Если БД доступна, она откроет базу данных, если нет, то создаст новую базу данных.
Если мы не передаем имя БД в качестве аргумента, то создается временная база данных в памяти, которая будет удалена после завершения сеанса. Здесь у меня нет никакой базы данных, поэтому я создам новую БД, упомянув имя db в качестве аргумента. Как только вы подключитесь к сеансу, вы можете запустить команду .databases, чтобы увидеть, какой файл прикреплен к базе данных.
$ sqlite3 /home/tecmint/test # создание тестовой базы данных в /home/tecmint
Теперь давайте создадим пример таблицы, выполнив следующие запросы.
# create table
sqlite> CREATE TABLE employee(
Name String,
age Int);
# Insert records
sqlite> insert into employee(Name, age)
VALUES (‘Tom’,25),
(‘Mark’,40),
(‘Steve’,35);
Вы можете запустить команду .tables, чтобы вывести список таблиц в базе данных.
Установка браузера SQLite в Ubuntu
Теперь, когда мы как установили и настроили sqlite3, мы также установим sqlite browser. Это простой графический инструмент для управления базами данных sqlite.
Вы можете запустить приложение из меню «Пуск» или из терминала. Для запуска браузера из терминала выполните следующую команду.
Удаление SQLite и браузера SQLite
Для удаления SQLite, так и SQLite browser потребуется выполнить следующую команду.
$ sudo apt —purge remove sqlite3 sqlitebrowser
Вот и все. Если у вас есть какие-либо отзывы или советы, пожалуйста, используйте раздел комментариев, чтобы опубликовать их.
Как установить SQLite на Debian 10
Как установить SQLite на Debian 10
В этом руководстве мы покажем вам, как установить SQLite в Debian 10. Для тех из вас, кто не знал, SQLite — это легкая программа для работы с базами данных, работающая из командной строки. Это один из почти эффективных механизмов баз данных на планете. Отчасти благодаря тому, что написано на языке C, что делает его очень эффективным в управлении активами системы.
В этой статье предполагается, что у вас есть хотя бы базовые знания Linux, вы знаете, как использовать оболочку, и, что наиболее важно, вы размещаете свой сайт на собственном VPS. Установка довольно проста и предполагает, что вы работаете с учетной записью root, в противном случае вам может потребоваться добавить ‘ sudo ‘ к командам для получения привилегий root. Я покажу вам пошаговую установку SQLite на Debian 10 (Buster).
Установите SQLite на Debian 10 Buster
Шаг 1. Перед установкой любого программного обеспечения важно убедиться, что ваша система обновлена, выполнив следующие apt команды в терминале:
Шаг 2. Установка SQLite в Debian 10.
Теперь выполните следующую команду, чтобы установить SQLite в системе Debian Linux:
Как только это будет завершено, проверьте версию:
Для начала sqlite3 выполните следующую команду:
SQLite 3 и SQLiteBrowser, как установить их в Ubuntu
DB4S или SQLiteBrowser очень подходят как для пользователей, так и для разработчиков, которые хотят создавать, искать и редактировать базы данных. DB4S использует знакомый интерфейс, похожий на электронную таблицу., и избавляет от необходимости изучать более сложные команды SQL.
Элементы управления и мастера SQLiteBrowser доступны пользователю для:
Установите SQLite 3 и SQLiteBrowser в Ubuntu
Установить SQLite 3
Для начала мы будем установить эту СУБД. Настройка SQLite проста по сравнению с другими популярными базами данных, такими как MySql, Postgresql и т. Д. Прежде чем продолжить установку, нам необходимо обновить список доступного программного обеспечения. Для этого откроем терминал (Ctrl + Alt + T) и выполним команду:
к установить пакет При необходимости следующая команда, которую мы собираемся выполнить, будет следующей:
После установки мы можем проверьте установку, запустив сеанс sqlite 3. Для этого в том же терминале достаточно написать:
Как видно на изображении выше, SQLite 3 успешно установлен и работает с версией 3.31.1. Хотя сегодня есть более актуальные версии, это тот, который был установлен на моем компьютере из репозитория Ubuntu
Создать образец базы данных и таблицы
База данных SQLite 3 будет храниться в виде файла в нашей локальной файловой системе.. Мы сможем создать базу данных при запуске сеанса sqlite, указав имя базы данных в качестве аргумента.
При запуске команды, если база данных доступна, она откроет эту базу данных. Если мы не включим имя базы данных в качестве аргумента, будет создана временная база данных в памяти, которая будет удалена после завершения сеанса.
В этом примере мы собираемся создать базу данных под названием test в папке / home / entreunosyceros (это имя домашней папки моего пользователя)
После создания мы можем посмотреть, к какой сессии базы данных вы подключены с помощью этой другой команды:
Чтобы продолжить пример, давайте создать образец таблицы выполнение следующих запросов:
Теперь мы можем запустите команду .tables чтобы перечислить таблицы, доступные в базе данных, к которой мы подключены:
На этом этапе мы можем распечатать содержимое таблицы, созданной для этого примера:
Установить SQLiteBrowser
После того, как мы установили и создали образец базы данных с sqlite3, мы собираемся установить SQLiteBrowser. Есть простой инструмент с графическим интерфейсом для управления нашими базами данных sqlite. Для этого выполним в терминале (Ctrl + Alt + T):
После установки мы можем запустить приложение из начального меню. Мы также можем запустить его, открыв терминал (Ctrl + Alt + T) и выполнив команду:
После запуска программы откроется графический интерфейс, из которого мы можем выберите базу данных, которую мы создали ранее, из терминала:
Удалите SQLite 3 и SQLiteBrowser
к удалить как SQLite, так и SQLiteBrowser, нам нужно только открыть терминал (Ctrl + Alt + T) и выполнить в нем команду:
Он может узнать больше о SQLite на странице проектная документация, y Если вам интересно узнать больше о SQLiteBrowser, вы можете найти информацию в сайт этой программы.
Содержание статьи соответствует нашим принципам редакционная этика. Чтобы сообщить об ошибке, нажмите здесь.
Полный путь к статье: Убунлог » Ubuntu » SQLite 3 и SQLiteBrowser, как установить их в Ubuntu
Install SQLite and SQLite Browser on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
SQLite is a lightweight database software. It is a command line application. You must use the command line or SQLite API on other programming languages to use SQLite database. SQLite has a graphical front end SQLite Browser for working with SQLite databases graphically.
SQLite 3 is the latest version at the time of this writing. SQLite 3 is available in the official package repository of Ubuntu 18.04 LTS. SQLite Browser is also available in the official package repository of Ubuntu 18.04 LTS.
In this article, I will show you how to install SQLite 3 and SQLite Browser on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS. I will also show you some of the basic queries of SQLite 3. Let’s get started.
Installing SQLite 3
First update the apt package repository cache with the following command:
The apt package repository cache should be updated.
Now to install SQLite 3, run the following command:
SQLite 3 should be installed.
Now you can check whether SQLite 3 is working with the following command:
Installing SQLite Browser
Run the following command to install SQLite Browser:
SQLite Browser should be installed.
Using SQLite using SQLite Browser
Now you can go to the Application Menu and search for SQLite Browser. You should see a database icon as marked in the screenshot below. Click on it.
SQLite Browser should start as you can see in the screenshot below.
Getting Started with SQLite 3 using SQLite Browser
In this section, I will show you the basics of SQLite 3 database with SQLite Browser graphical user interface.
First click on New Database to create a new database using SQLite Browser.
You should see the following dialog window. Type in a filename and save it somewhere on your filesystem.
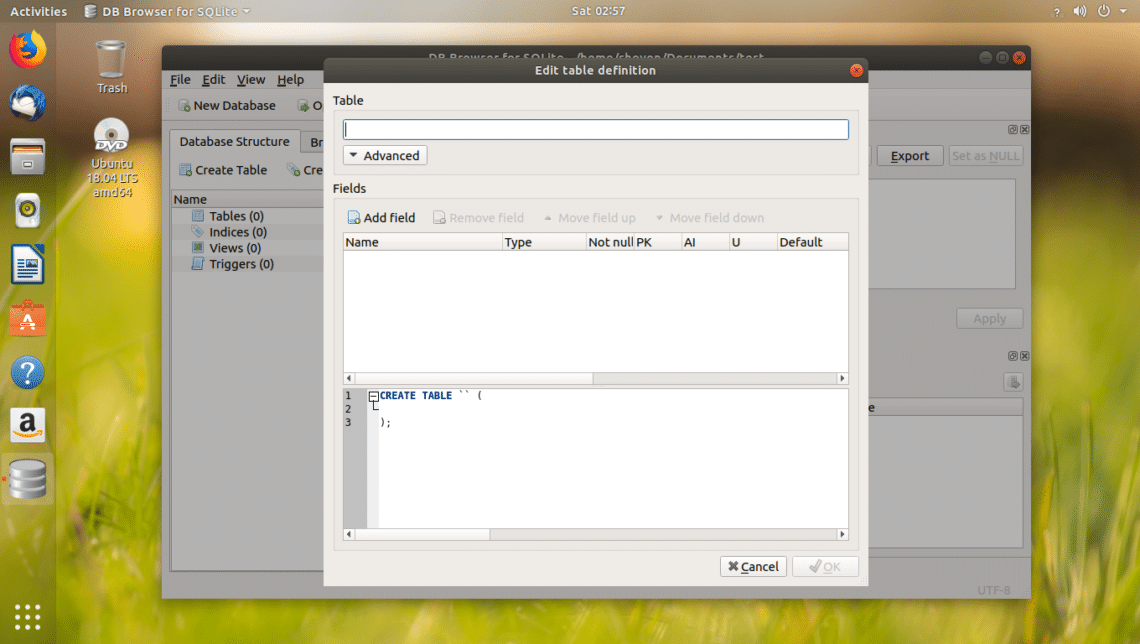
Now you should the following window. Using this window, you can create your first SQLite 3 table.
Enter the name of the table. If you want to follow along, users table it is.
Now you can click on Add field button to add as many fields or columns on your table.
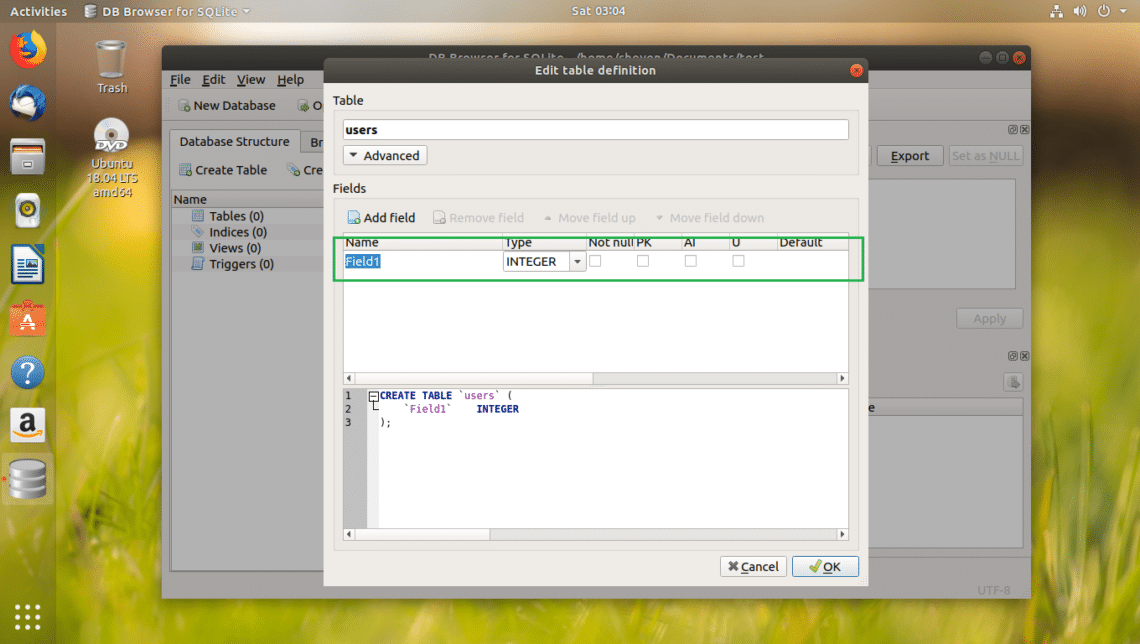
Once you click on Add field button, you should see a new field as marked in the screenshot below.
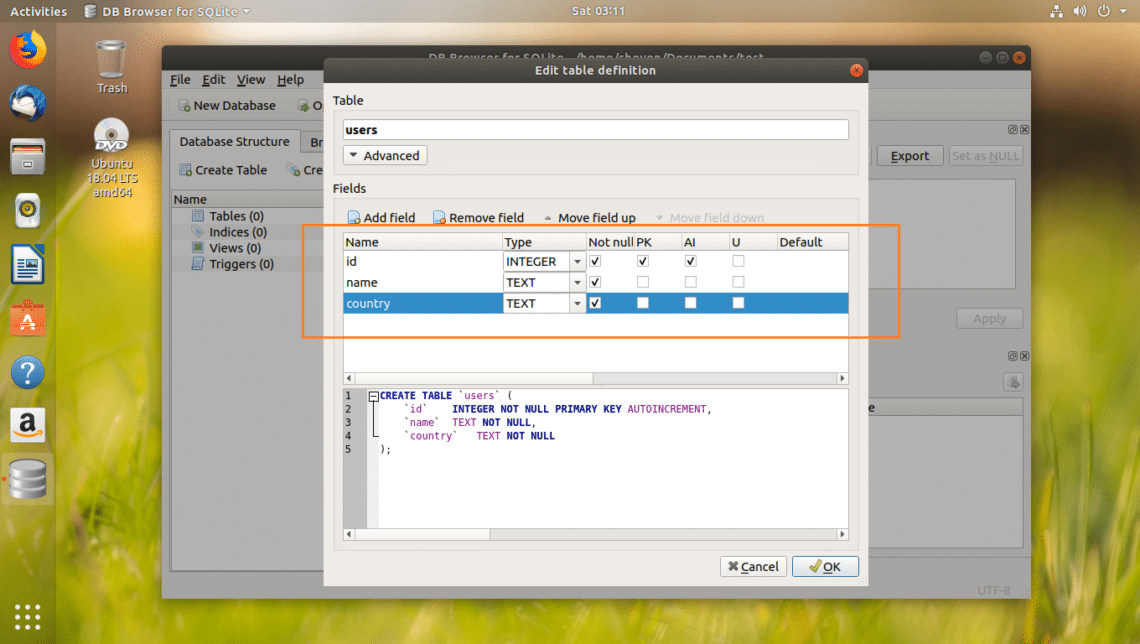
I named the field id, changed the Type to INTEGER, checked the Not null, PK (Primary Key), AI (Auto Increment) checkboxes.
I added name and country field, set their Type to TEXT and checked the Not null checkboxes.
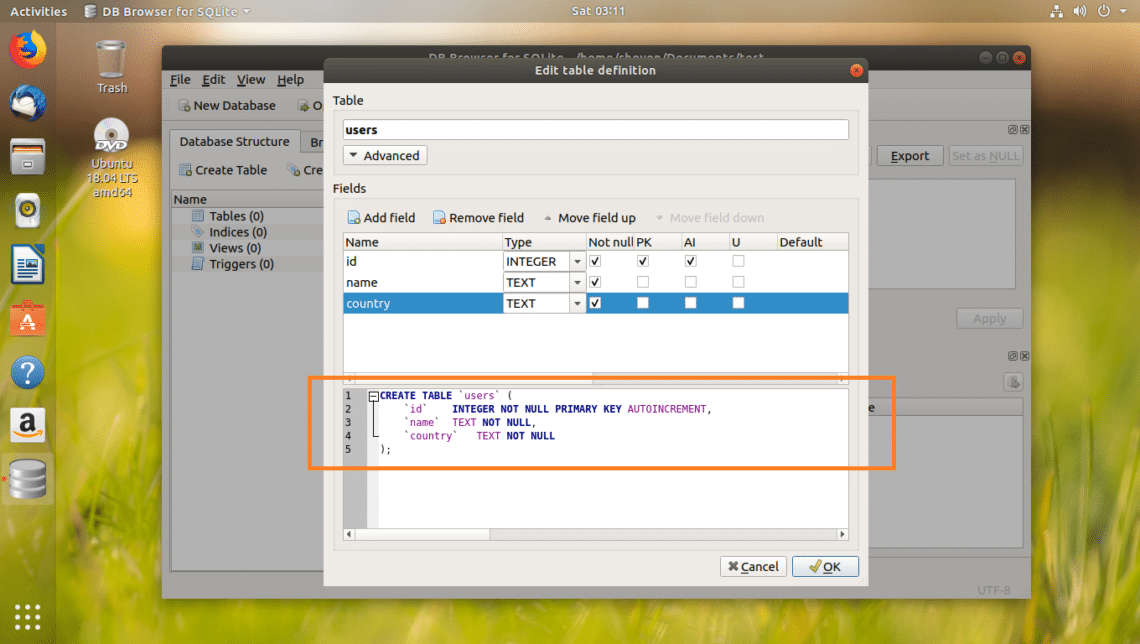
In the marked section of the screenshot below, you can find the SQL code. You can run this code in the SQLite 3 command line interface and create an identical users table as well. SQLite Browser is an awesome tool to lean SQLite as well.
Once you’re happy with your table, click on OK.
users table should be created.
Now I will show you how to insert data into the users table.
First go to the Browse Data tab as marked in the screenshot below.
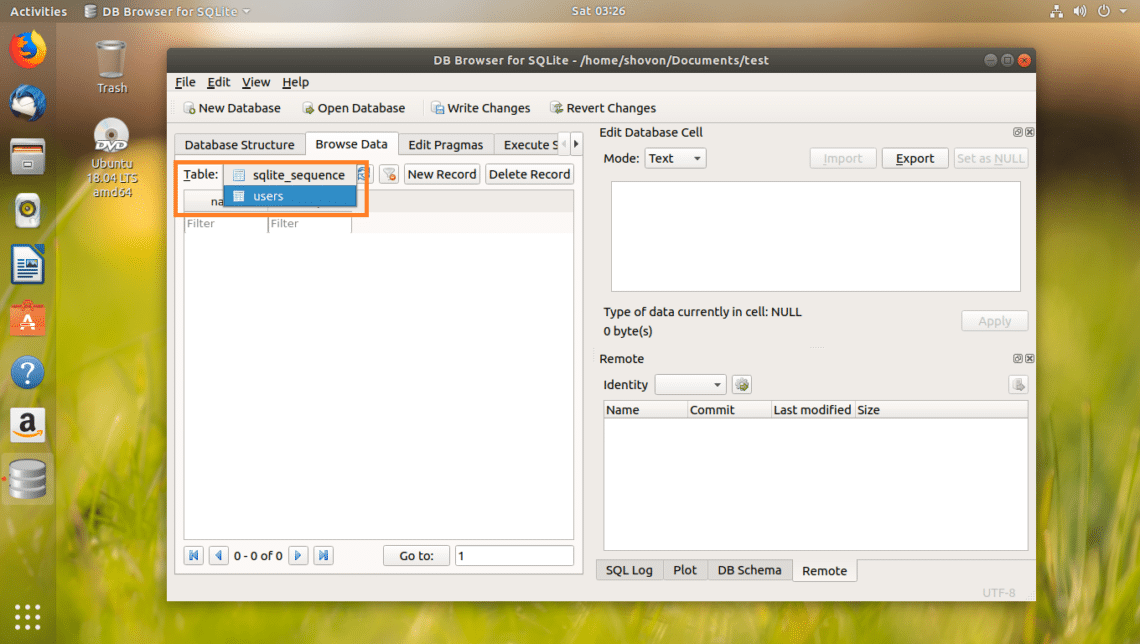
Now select the users table from the marked section of the screenshot below.
Once users table is selected, click on New Record button to add a new row or data into the table.
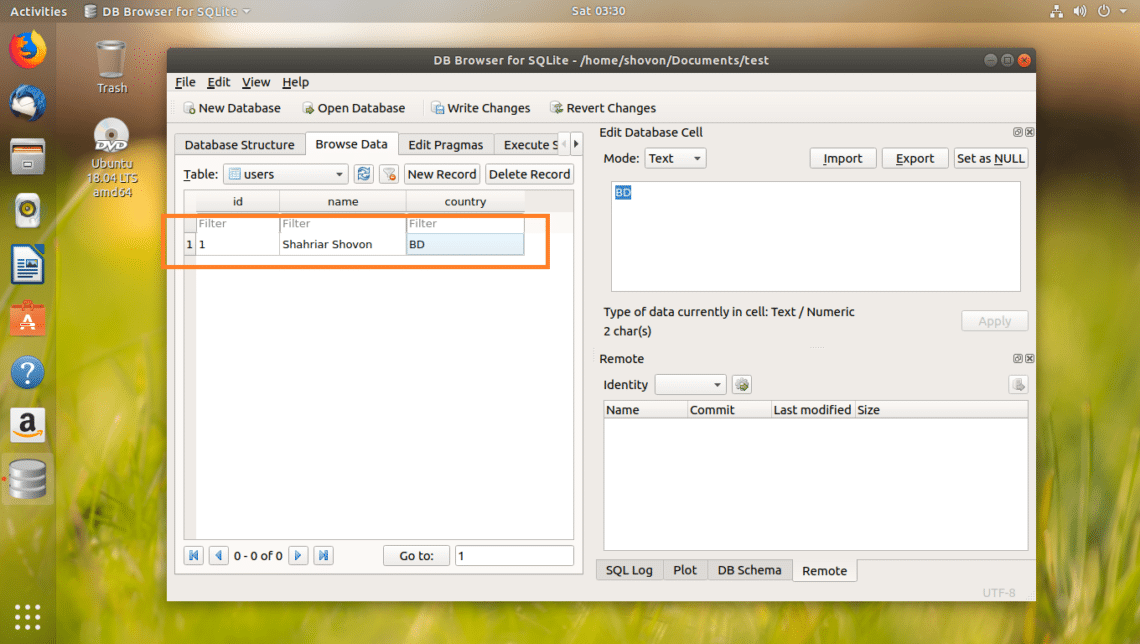
The id should be auto generated. The name and the country field should be blank. Click on each of them and type in your desired data.
As you can, I added a new row to the users table.
Now to save the changes, click on Write Changes button as marked in the screenshot below.
The changes should be written to the file on your filesystem.
If you want, you can execute SQL statements on SQLite Browser as well.
To execute SQL statements, first go to the Execute SQL tab as marked in the screenshot below.
Enter your SQL statements in the marked section of the screenshot below.
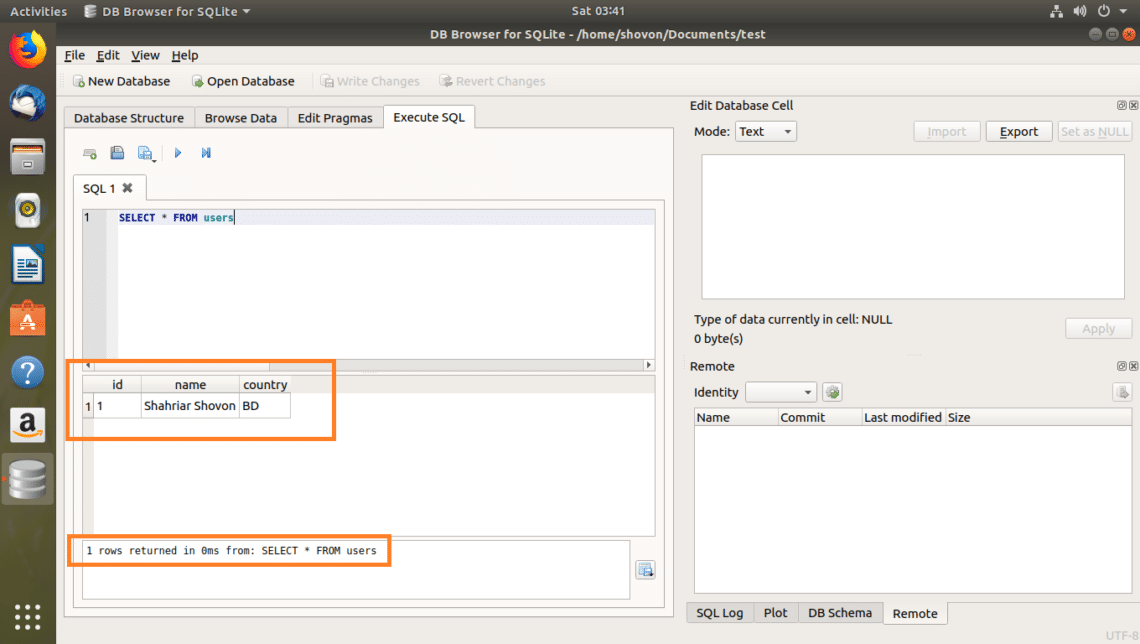
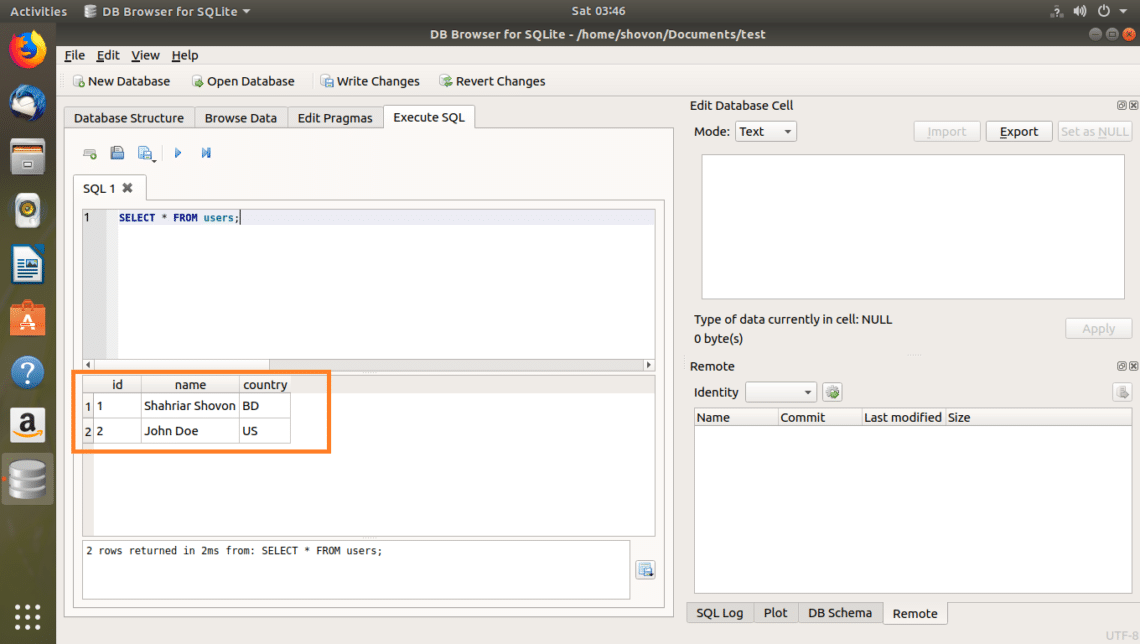
I wrote a simple SQL statement, SELECT * FROM users.
Now if you want to execute the SQL statement, click on the play button as marked in the screenshot below. You can also press F5 or + r
As you can see, the data is returned.
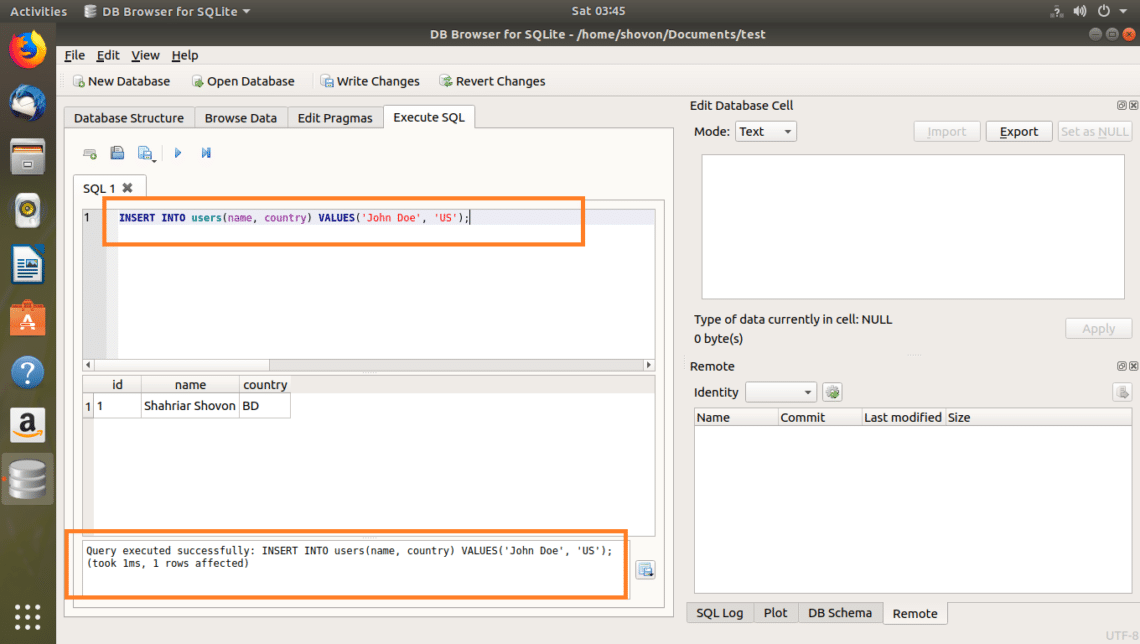
You can insert into the users table with the following SQL command:
INSERT INTO users(name, country) VALUES(‘John Doe’, ‘US’);
Now if you run SELECT * FROM users again, you should see the new data.
Exporting SQLite Database using SQLite Browser
You can export the SQLite database using SQLite Browser.
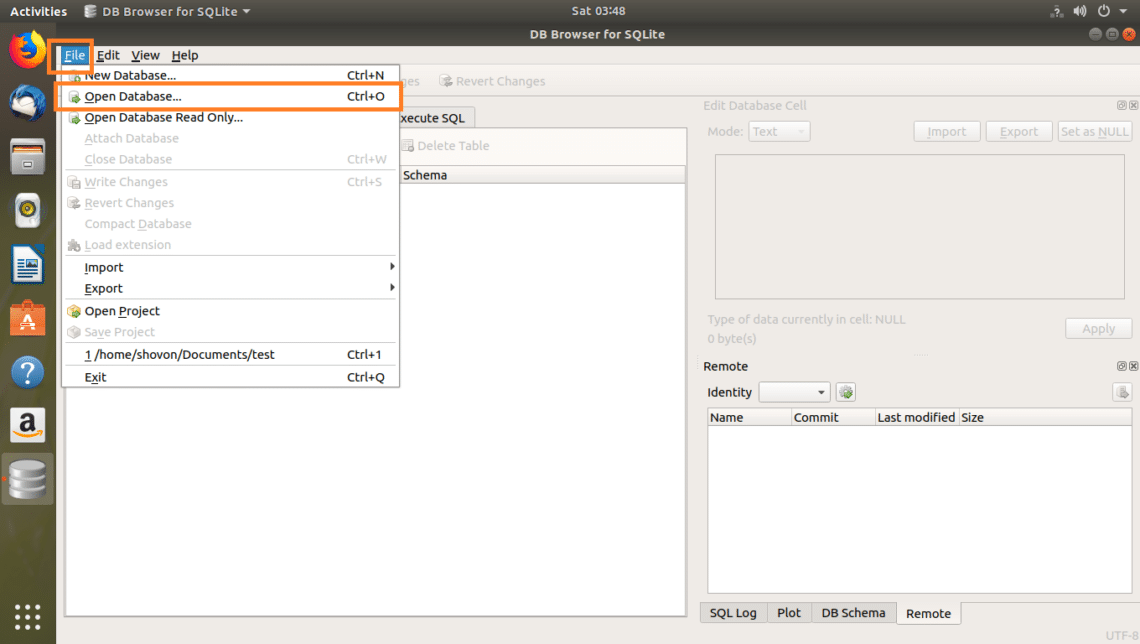
First open the SQLite database from File > Open Database…
Now select your SQLite database file and click on Open.
Your database should be opened.
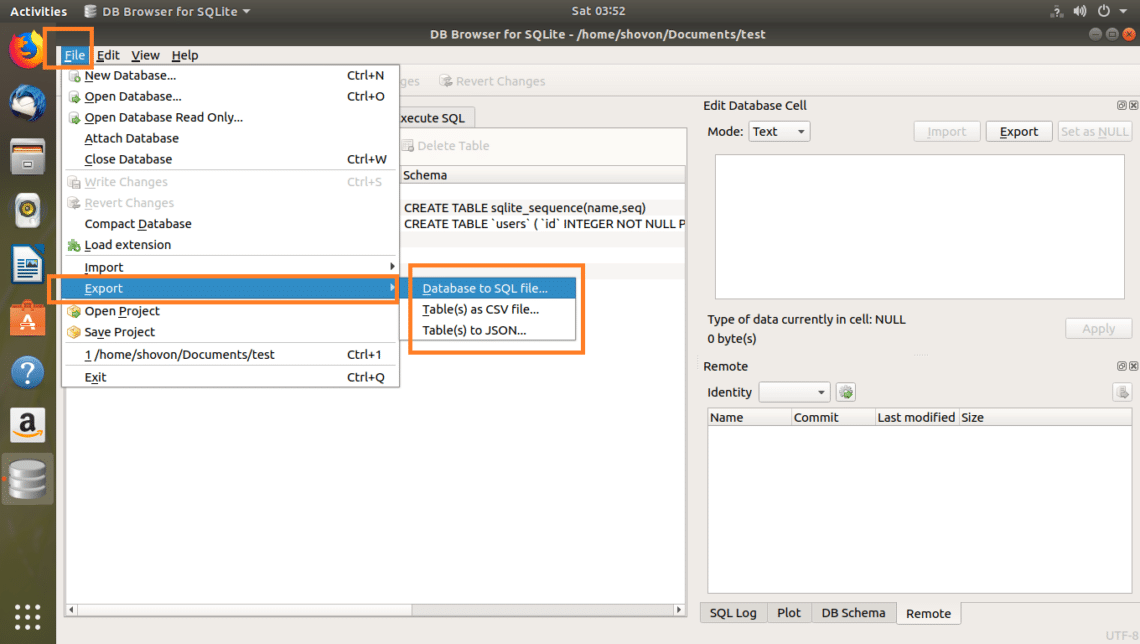
Now you can click on File > Export and then select either Database to SQL file… or Table(s) as CSV file… or Table(s) to JSON… to export the database to your desired format.
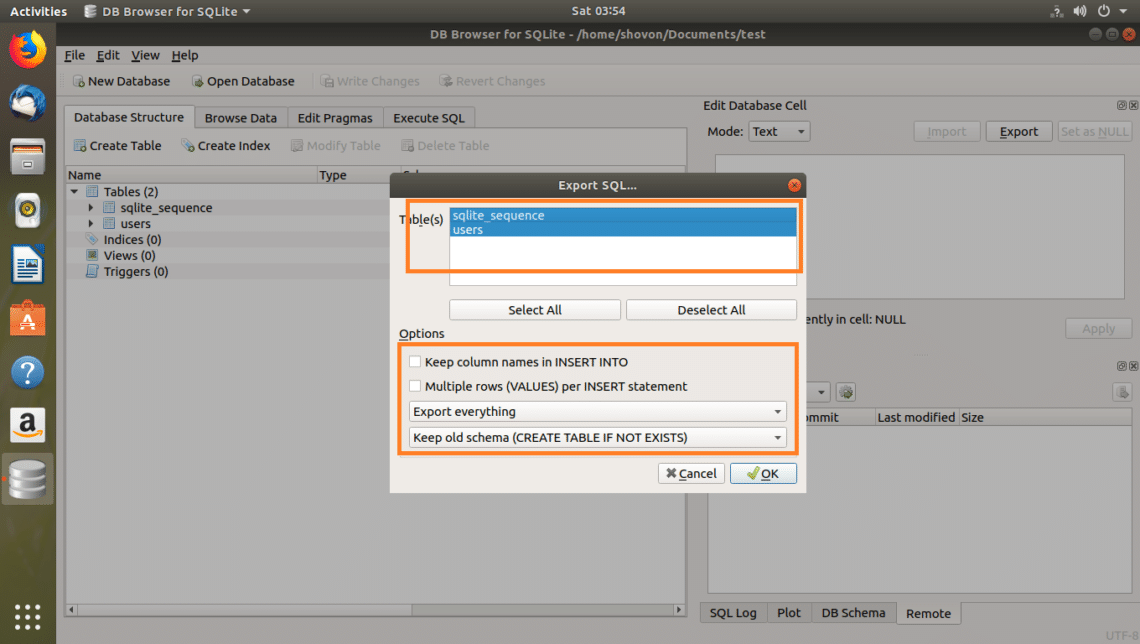
You should see the following window. Now select the tables that you want to export from the Table(s) section. By default, all the tables are selected.
You can also change some options to configure how the exported file should be formatted.
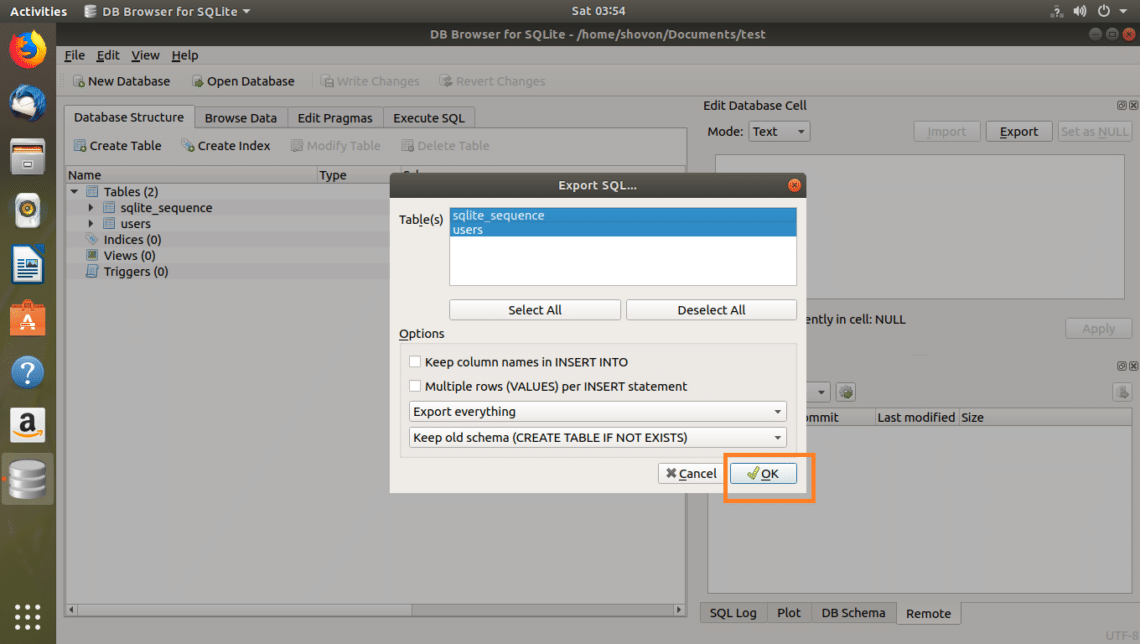
Once you’re happy, click on OK.
Now select the file path, type in a filename and click on Save.
The database should be exported, now click on OK.
As you can see, the database was exported as SQL.
So that’s how you install SQLite 3 and SQLite Browser on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS, and use SQLite Browser. Thanks for reading this article.
How to Install and Basic SQLite Use on Linux
In this article, We will see how to install SQLite (relational database) with its basic operations. What if I tell you that SQLite is likely used more than all other database engines combined. Yes, You heard it right. It is the most widely deployed database in the world with millions and billions of copies.
The reason behind this popularity is some unique characteristics that are unusual and which makes it different from many other SQL database engines like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, etc. Let’s get started with it. First, We will install it on Linux and later on cover basic database operations.
Installing Sqlite
To install on your Debian based (Ubuntu, Debian, etc.) machine execute below commands.
To install on your RPM-based (RHEL, CentOS, Fedora etc.) machine execute below commands.
You may also install SQlite using the DNF package manager:
Now Open a terminal and Execute «sqlite3», you will see the following lines with prompt.
The very first line shows the version and release date and time of sqlite3.
The second line tells to enter «.help» for instructions.
.help command list all the meta commands and their descriptions. These meta commands are also called «dot» commands because they are preceded by a dot.
Put «.help» to prompt
Before explaining these dot commands, let’s see some of the basic database operations.
First run «.quit» command to end the session.
Create Database
Execute below command on shell prompt.
It will create «example.db» (You can put your choice of name in place of «example.db») database file ( if not exists). If exists then open the database contained in the file.
The difference between «sqlite3» and «sqlite3 dbname.db» command is the first one will create a temporary database for the session and will expire when the session is closed.
Create Table
Let’s create a student table with attributes:
reg_no int(4)
Name varchar(20)
Marks int(3)
enter the following commands in terminal
It will create a student table with above attributes.
You can see the list of tables in the selected database by .table command
There is only one table student in my case.
You can also see the schema of the table using .schema table_name
Inserting Data
Let’s insert 3 records in the table
101, pradip, 87
102, Avinash, 86
103, Rakesh, 90
Enter the following command one by one
Fetching data
You can fetch data from table with select statement
It shows the result in default mode (list).
You can change the mode with .mode command
Delete, Alter, Drop etc have same syntax as sql.
We saw «.help» commands list all the dot commands. Let’s understand some other important commands.
Shows name of database selected.
List the tables in the selected database.
Shows the current settings
The Program is able to show the results of a query in eight different formats: «csv», «column»,»html»,»insert», «line», «list», «tabs», «tcl»..mode command is use to switch between these output formats.
You can use .separator command to change separator.
Writing results to a file
by default, It sends query results to standard output.
you can change this using «.output» and «.once» commands.
Or use the .once the command with file name if you want only the result of next query to be redirected.
We have successfully installed SQLite on Linux with basic operations. These operations are only a few out of all available. We can’t cover all of them in this article. If you find any difficulties in an installation or in any command, Let me know in the comment section.